
There will not be any difference in the mass of the piece of wood before and after the reaction if we weigh it before burning it and after ashes, water vapors, and CO2 are heated. Wood is broken down into ashes, water vapour, and carbon dioxide when it is burned. The law can be explained through various chemical reactions and even the combustion process. The law of conservation of matter states that the mass of substances in a closed system will remain constant, regardless of what processes are acting inside the.The law of conservation of mass requires that the reactant and product masses line up for a low-energy thermodynamic process. What Does Conservation of Matter Mean The law of conservation of matter is a fundamental principle of classical physics that states that matter cannot be created nor destroyed in any isolated system, but can only be converted from one form to another.In other words, the mass of any one element at the. This law states that matter cannot be generated or destroyed. The Law of Conservation of Mass dates from Antoine Lavoisiers 1789 discovery that mass is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions.

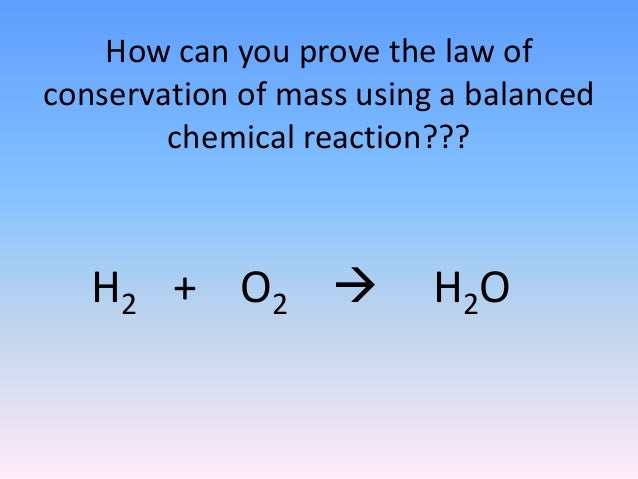
The mass of the wood before it burns must equal the mass of.

What is a Molecule? And Molecules of Elements The law of conservation of matter says that matter/mass can neither be created or destroyed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
